Snakes do have the ability to hear, but not in the way most people might think. Unlike mammals, they don't have external ears. Instead, their entire body acts as a sensory organ for detecting vibrations. Their scales are highly sensitive, picking up tiny movements in the ground and air, which are then sent to their inner ear.
The snake's jaw plays a key role in this process. The quadrate bone transmits low-frequency sounds to the inner ear, where specialized organs process these signals. Snakes can detect sounds in the range of 20-400 Hz, which means they can pick up human voices and other environmental noises.
This unique hearing system is crucial for snake survival. It helps them detect potential threats and locate prey. While it might seem strange to us, this method of "hearing" is perfectly suited to a snake's lifestyle and needs.
For those interested in learning more about how snakes perceive their environment, there's plenty of fascinating research available on the subject.
Snake Hearing Mechanism
Snakes have a unique way of picking up sounds that's quite different from humans. They don't have ears like we do, but they're still very good at sensing what's going on around them.
These reptiles use their whole body to "hear." Their scales are super sensitive and can feel tiny movements in the ground or air. When something makes a noise, like footsteps or leaves rustling, it creates vibrations. Snakes can feel these vibrations through their scales.
Once a snake feels these vibrations, its body sends the information to its inner ear. This part of the snake's anatomy is crucial – it changes those physical vibrations into signals the brain can understand. The snake's brain then figures out what these signals mean, helping the snake make sense of its surroundings.
This hearing system shows how well snakes have adapted to their environment. By using their body to sense vibrations, they can react quickly to potential threats or prey. It's a clever trick that helps them survive in the wild.
The way snakes hear is a great example of how animals can develop unexpected solutions to life's challenges. Their scale-based hearing might seem odd to us, but it works perfectly for their needs. It's just one of the many ways nature has come up with to help creatures thrive in their habitats.
Sound Frequencies Detected

Snakes' hearing abilities offer fascinating insights into how they perceive their surroundings. These reptiles can pick up sounds between 20-400 Hz, which is much lower than what humans can hear. This unique hearing range plays a big role in how snakes interact with their environment.
Studies show that snakes react differently to various sound frequencies:
- At around 1150 Hz, some snake species become more active.
- Between 150-300 Hz, which includes the range of human speech, snakes can hear people talking loudly or yelling.
- Ball pythons seem most responsive to sounds between 80-160 Hz.
This ability to detect specific sound frequencies helps snakes survive. They can hear potential prey or predators, making them more aware of what's happening around them. Interestingly, since human voices fall within their hearing range, snakes might be more tuned in to our presence than we previously thought. This shows just how complex and sophisticated snakes' sensory world really is.
Understanding these details about snake hearing sheds light on their behavior and how they interact with their surroundings. It's a reminder of the intricate ways animals adapt to their environments, often in ways we're just beginning to understand.
Jawbone and Vibration
Snakes have a remarkable ability to sense vibrations, thanks to their unique jaw structure. The snake's jawbone, particularly the quadrate bone, serves as a pathway for low-frequency sounds to reach the inner ear directly. This allows snakes to pick up on subtle ground movements with incredible accuracy.
Unlike many animals, snakes don't rely on typical hearing methods. Instead, they use their jaw to conduct vibrations. When the ground shakes, even slightly, the snake's lower jaw catches these tremors. The quadrate bone then relays this information to the inner ear.
This specialized system gives snakes a distinct advantage in the wild. They can detect nearby prey or approaching predators without seeing them. In environments where staying hidden is crucial, this skill can mean the difference between eating and being eaten.
| Feature | Function |
|---|---|
| Jawbone | Captures ground vibrations |
| Quadrate Bone | Passes vibrations to inner ear |
| Ground Vibration Detection | Picks up low-frequency sounds |
| Vibration Response | Helps locate food and threats |
This unique sensory system showcases nature's ingenuity in adapting creatures to their environments. For snakes, it's a key tool in their survival toolkit, allowing them to thrive in diverse habitats across the globe.
Inner Ear Structure
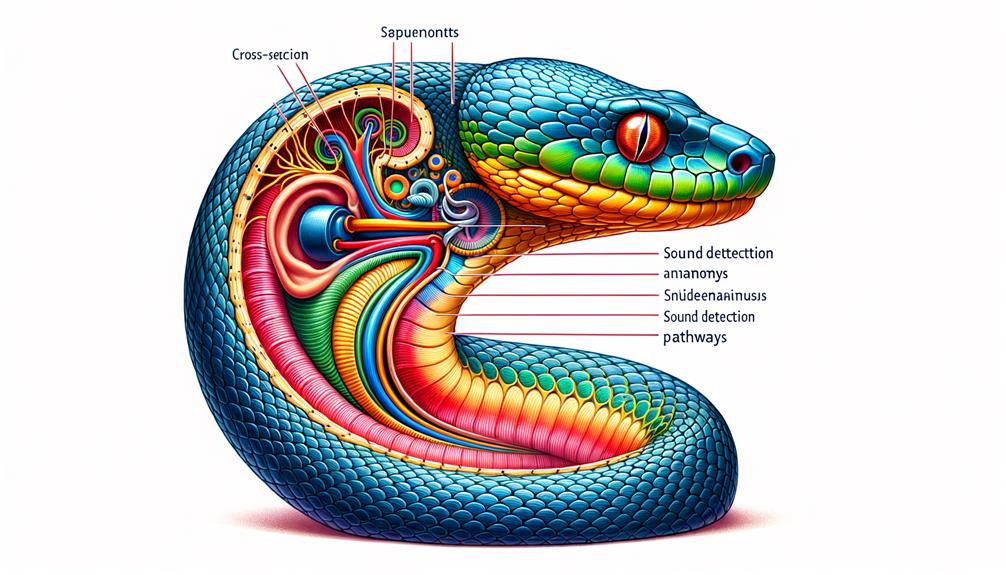
Snakes have a remarkable inner ear setup, despite their lack of external ears. This internal system is crucial for picking up both sound waves and vibrations in their surroundings.
The inner ear of a snake connects directly to its brain through the auditory nerve. This setup allows snakes to hear sounds in their environment, particularly those with low frequencies.
Two key components make up this system:
- The cochlea: A coiled structure that detects sound waves
- Otolith organs: Specialized for sensing vibrations and movement
This dual-purpose system helps snakes adapt well to their habitats, where low-frequency sounds are common. The auditory nerve carries electrical signals from the inner ear to the brain, allowing snakes to react to what they hear.
It's a common misconception that snakes are deaf. In reality, their inner ear structure is highly specialized, giving them an accurate sense of their surroundings. This intricate system showcases how well these reptiles have adapted to their environments.
The sophistication of a snake's inner ear highlights just how complex and precise their sensory abilities are. It's a testament to the incredible ways animals evolve to thrive in their specific habitats.
Common Misconceptions

Contrary to what many think, snakes aren't deaf. They actually have a unique hearing system that picks up both air and ground vibrations. People often assume snakes can't hear because they don't have visible ears, but recent studies show they've developed inner ear parts specifically for catching low-frequency sounds and vibrations.
Research has shown that snakes use their jaw bones as a kind of hearing aid. When sound waves hit the ground, they create vibrations. These travel through the snake's body to its inner ear, allowing it to sense the sound. This process is quite impressive and shows how well snakes have adapted to their surroundings.
The structure of a snake's inner ear is different from what we see in mammals, but it works just as well. There's a small bone called the columella in the snake's inner ear that's key to sending vibrations to the cochlea. Learning about these mechanisms not only corrects the myth but also highlights the fascinating ways snakes have evolved to thrive in their environments.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a Snake Hear You?
Snakes can pick up on sounds, but not in the way we do. They're tuned into low-frequency noises, meaning they might react to a shout or yell, but won't catch your regular chitchat. Their main method of hearing isn't through ears like ours. Instead, they feel vibrations through their body, which helps them sense what's happening around them. So while a snake might not hear your whispers, it could definitely feel the thump of your footsteps nearby.
Are Snakes Unable to Hear as They Lack Ears Like Us True or False?
While snakes don't have external ears like humans, they're not entirely deaf. These reptiles pick up sound waves through their jawbones, which transfer vibrations to their inner ears. This unique hearing method allows them to sense their surroundings and detect potential prey or predators. So, it's not accurate to claim snakes can't hear at all – they just do it differently than we do.
Do Snakes React to Noise?
Snakes are more attuned to their surroundings than many people realize. These reptiles pick up on sound waves traveling through the earth and air. Their entire body acts like a sensor, feeling vibrations that their nervous system then interprets. This ability helps snakes respond to key sounds in their environment, including those made by humans. While they might not hear in the same way we do, snakes are certainly aware of the noises around them, using this information to navigate their world and stay safe from potential threats.
Does a Snake Hear With Its Tongue?
Snakes don't use their tongues for hearing. Instead, they rely on this forked appendage as a super-sensitive detector for chemical signals in their surroundings. It's like a built-in analyzer, helping them make sense of their environment. When it comes to picking up sounds, snakes have a different trick up their sleeve. They've got a special structure in their inner ear that detects vibrations, allowing them to sense what's going on around them. So while a snake's tongue is crucial for gathering information, it's not involved in the hearing process at all.



